What is a RESET IC?
1. What is a RESET IC?
The RESET IC (voltage detector/power supply monitoring IC) is a type of power supply IC. Mainly used to monitor the power supply voltage of electronic equipment, RESET ICs monitor/detect whether a voltage has reached a specified value (threshold value).
Familiar equipment uses many RESET ICs. RESET ICs monitor power supply voltages to ensure every piece of electronic equipment such as office equipment and large household electrical appliances both starts and stops safely. While MCUs (micro controller units/ built-in resetting function) or other devices may also perform such functions, functions such as those for safety protection can only be performed by RESET ICs. The following sections explain the details of what RESET ICs can do.
※Other names for RESET ICs include voltage detectors and supervisors.
2.What RESET ICs can do
Start/stop MCUs safely
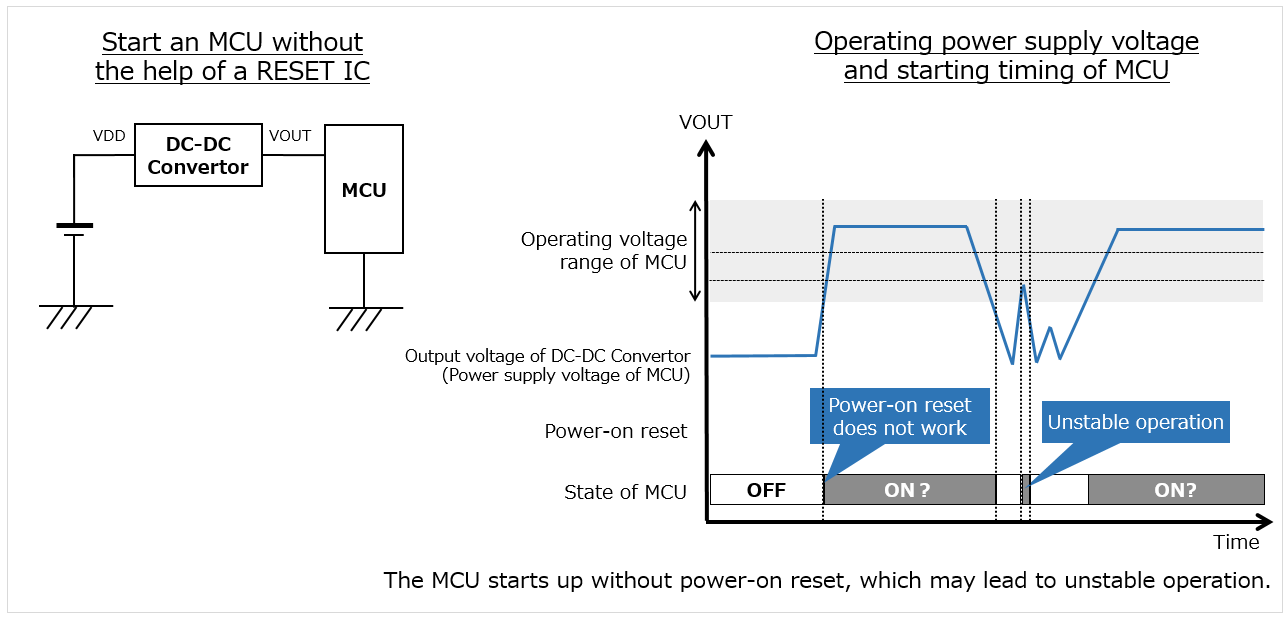
Many types of electronic equipment are equipped with microcontroller units (hereafter, MCUs). MCUs serve as brains that control the operation of electronic equipment.
Each MCU has a specified minimum operating voltage. If an MCU is started when the power supply voltage is lower than this level or is unstable, erroneous operation occurs, and the equipment itself may also make errors or break down.
To operate stably, an MCU must perform power-on reset (POR)* upon startup. An unstable rise in the power supply voltage sometimes causes the malfunction failure of POR built into the MCU, which may lead to unstable operation after starting.
* Power-on reset: An operation that initializes elements in the MCU, such as registers, upon startup.
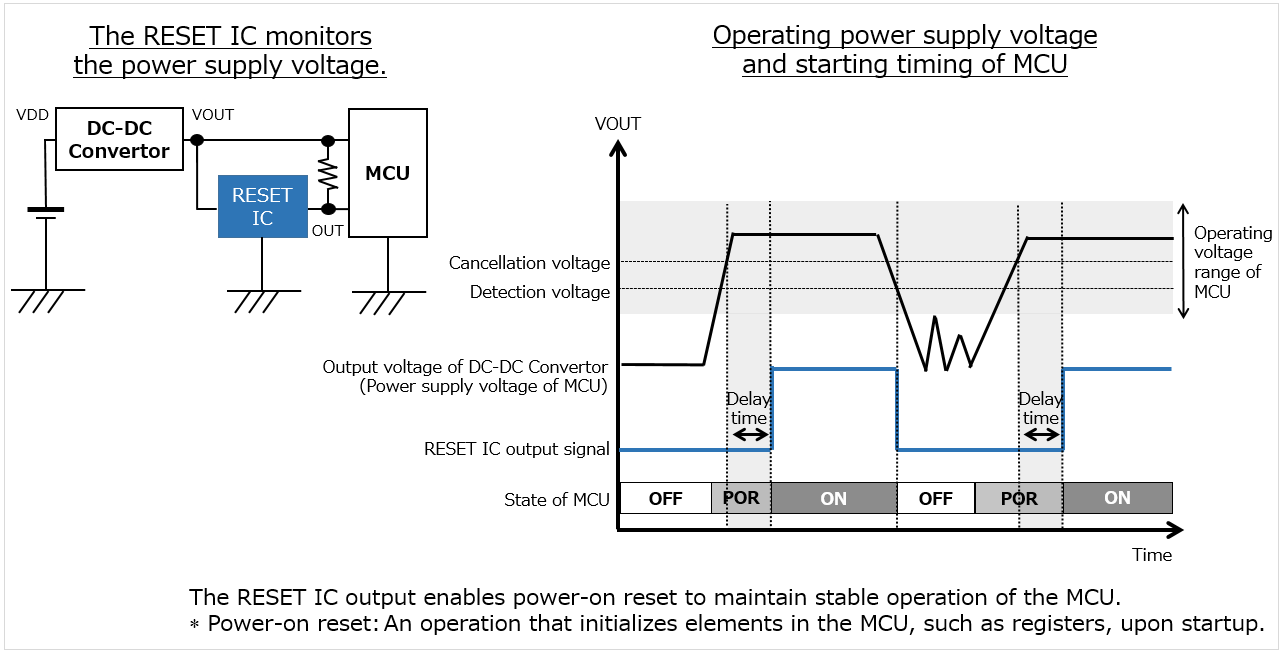
A RESET IC monitors the power supply IC output voltage, detects if it exceeds the operating voltage of the MCU, and then cancels the reset signal to the MCU in order to start the MCU.
In addition, by setting a delay time, a RESET IC can keep the MCU in the reset state during the time period that the MCU needs for power-on reset.
There are two output types for resetting: CMOS output and open drain output. Typical examples refer to open drain output.
When the power supply voltage of the MCU drops to be close to its minimum operating voltage, the RESET IC instantly outputs a reset signal to safely shut down the MCU.
MinebeaMitsumi's long-selling RESET ICs
Extend the battery life of a device
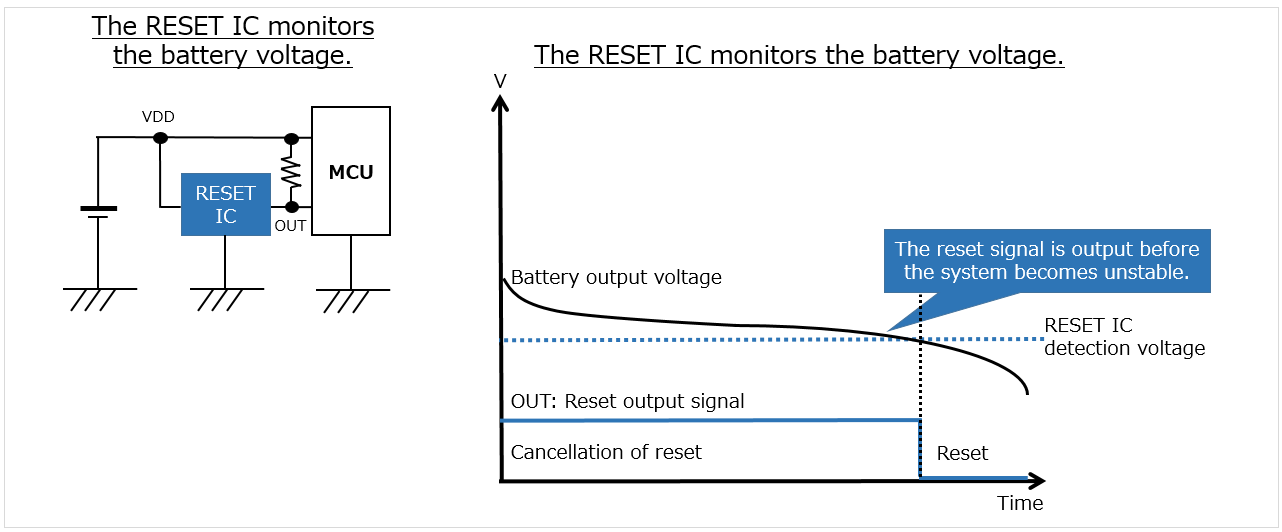
When the residual quantity approaches zero, the output voltage of a battery drops sharply.
For this reason, to avoid equipment malfunction/failure, the operation of battery-powered equipment must be controlled before the drop in battery output voltage accelerates.
A RESET IC monitors the output voltage of a battery (battery voltage). This IC outputs a reset signal before the battery voltage drops sharply to help control equipment operation.
In addition, using a precision voltage detection RESET IC can extend the battery life of a device.
The RESET ICs best for battery-powered equipment High detection accuracy: ±0.5%/Detecting voltage: 0.8 V or higher
Automotive use Rated voltage: 40 V; RESET IC with a separate sensing pin best for monitoring battery voltage
Automotive use Rated voltage: 40 V; RESET IC with separate 2-ch sensing pins best for monitoring battery voltage
5 to 10 V detection Voltage
Series
PST122A
Use for making redundant MCU systems
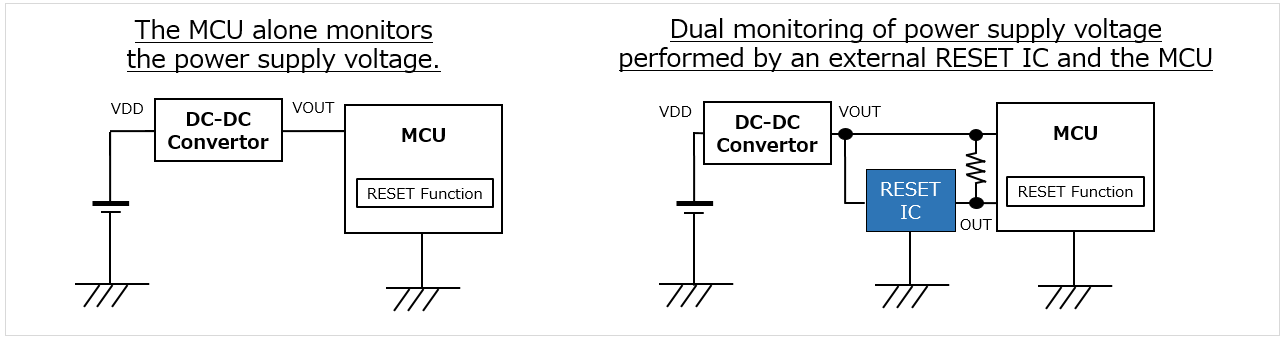
Even if an MCU with a built-in resetting function is used, some cases require the use of a RESET IC.
For example, for equipment that is required to meet high safety standards, such as automotive and industrial equipment, monitoring the power source with an MCU alone is not sufficiently safe in some cases.
A highly redundant system can be configured using a RESET IC as a failsafe mechanism for the case in which the MCU malfunctions and fails to monitor the power supply.
Contributing to making safe systems, RESET ICs respond to various needs.
Monitoring rises in voltage
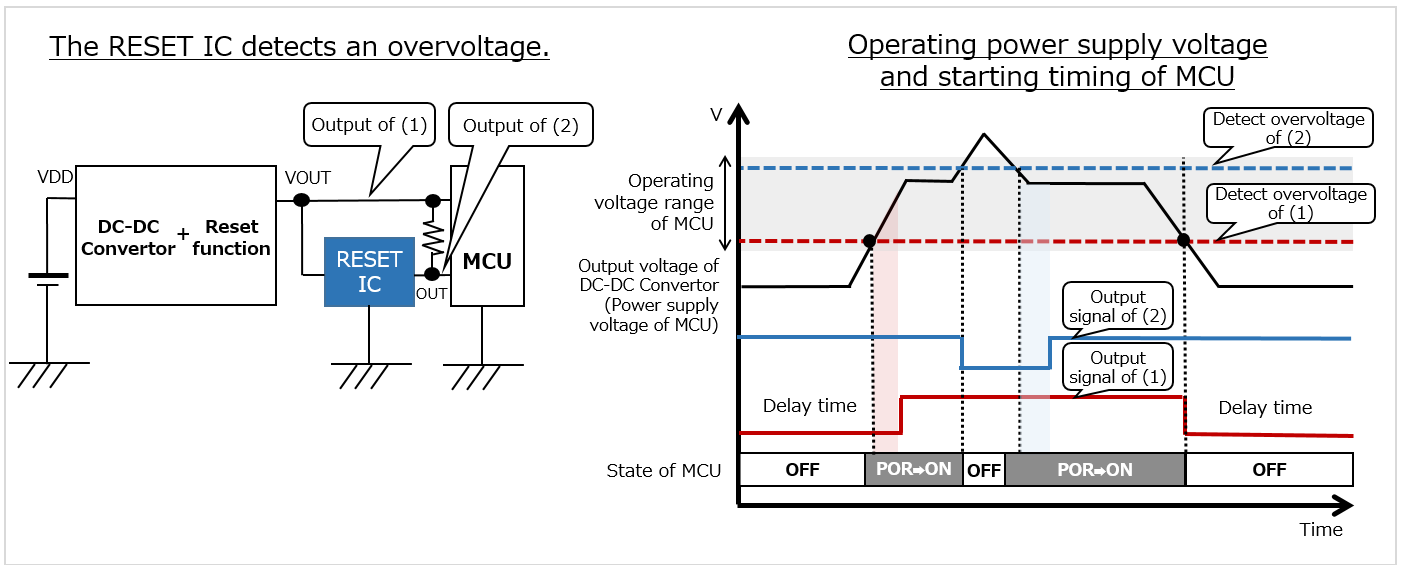
RESET ICs are also used for detecting rises in voltage (= overvoltage).
Mainly automotive equipment requires overvoltage detection.
This is because, when the supply power voltage from a car battery rises for some reason, an overvoltage detection function can protect the system's essential core parts (such as MCUs) from malfunctioning and failure.
While the A/D converter (ADC) in an MCU can easily detect an overvoltage, automotive equipment, for which safety is essential, often requires installing an overvoltage detection mechanism in addition to an MCU. In such a case, there are various methods, such as using a composite IC or other devices with an overvoltage detection function, or configuring a voltage detection circuit with a comparator or the like. Using a RESET IC is another effective method.
As shown in the block diagram below, a RESET IC can monitor the rise/fall in voltage as a mechanism independent of the MCU. This circuit is simpler than one with a comparator. In addition, using a RESET IC with a function for detecting the rise in voltage with high precision enables more reliable overvoltage detection.
Automotive use Rated voltage: 40 V; RESET IC with a separate sensing pin best for monitoring battery voltage
Automotive use Rated voltage: 40 V; RESET IC with separate 2-ch sensing pins best for monitoring battery voltage
5-10V detection Voltage
Series
PST122A
Securing a stable range by eliminating the undefined region
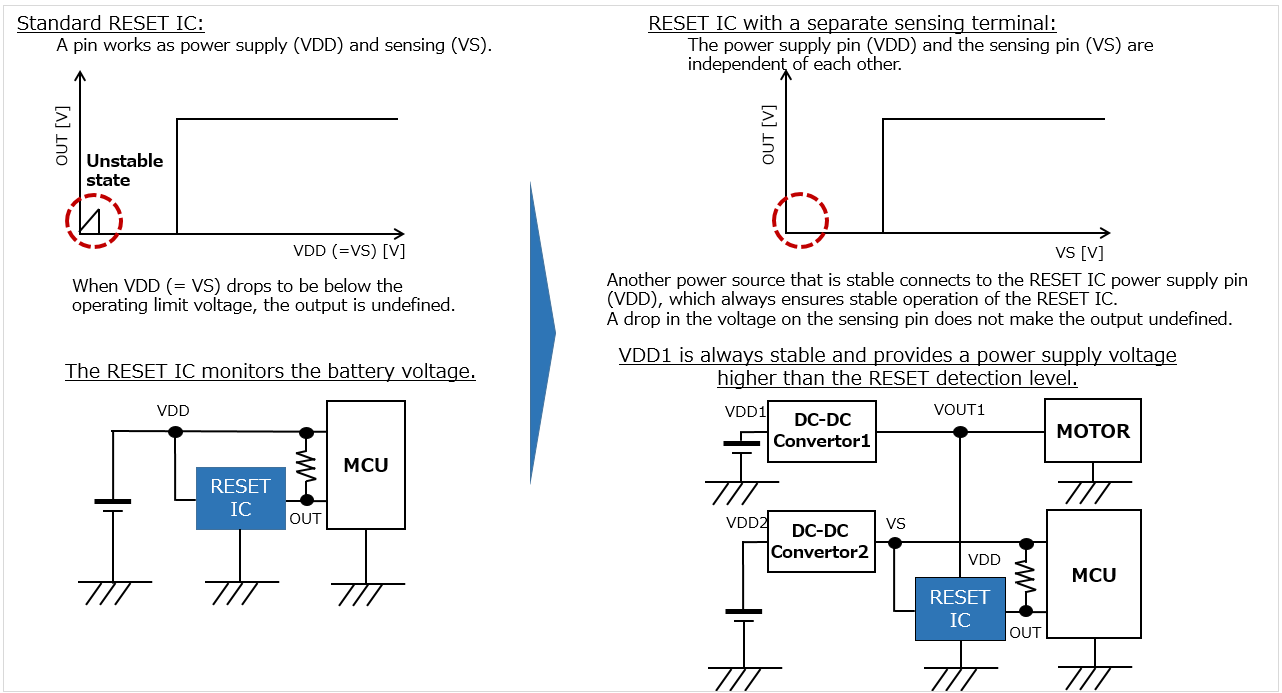
Just as an MCU has an operating voltage range, a RESET IC has its own voltage range in which it can operate stably.
A standard RESET IC uses the power supply voltage subject to monitoring as its own power supply. For this reason, when the power supply voltage to be monitored becomes lower than the operating voltage range of the RESET IC, the RESET IC cannot operate normally, and an undefined condition (in which it is unable to maintain reset detection) occurs, which may cause the MCU to malfunction.
This problem prominently occurs when monitoring a voltage of approximately 1 V, which is close to the minimum operating voltage that may trigger resetting.
Such a problem can be resolved by using a RESET IC with a separate sensing pin, which has an input pin for the power supply voltage to be monitored and another pin for the RESET IC's power supply.
Controlling power-off sequences
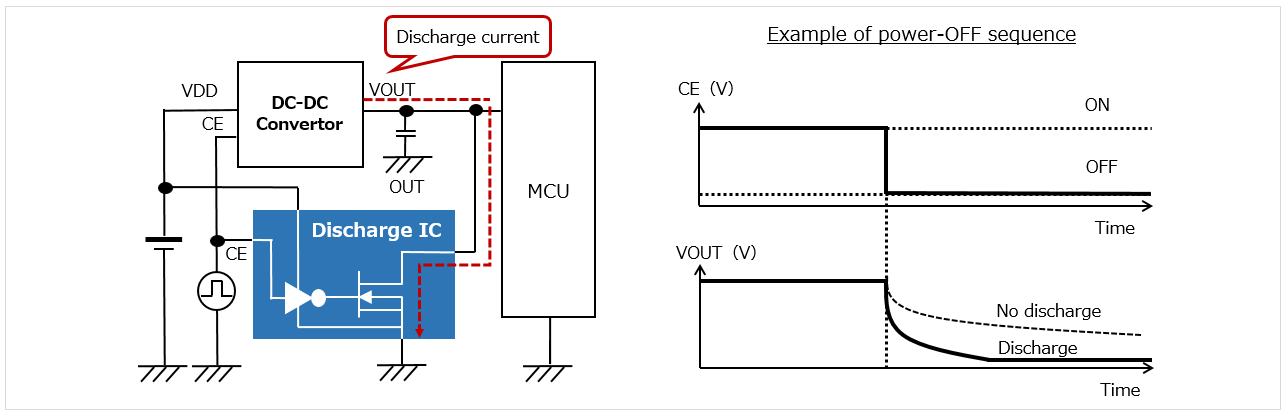
Many electronic devices are equipped with MCUs and similar ICs with multiple power lines. Power up/down procedures must be performed in the specified order or a breakdown/malfunction may occur.
A RESET IC monitors voltage. Some RESET ICs designed to have an open-drain output pin are sometimes used to assist in power-off sequences.
However, the open-drain pin of a RESET IC has a large ON resistance, which means it takes a long time to discharge an external device.
ICs specialized in controlling power-off sequences
Discharge IC
As indicated by its name, a discharge IC is used to discharge output capacitance.
Many electronic circuits are designed to have a discrete FET or a RESET IC (open-drain type) to discharge output capacitance.
Responding to the market's request for a simple power-off sequence control method, MinebeaMitsumi is mass-producing discharge ICs consisting of a transistor and an inverter.
”Discharge IC” that discharges the output capacitance of a power supply IC
3.Reset IC of MinebeaMitsumi
Standard RESET IC
| Configuration example | Output logic | Maximum rating | Series type | Output type |
Delay time |
Separate sensing terminal |
Manual reset |
Series (package) |
Single function reset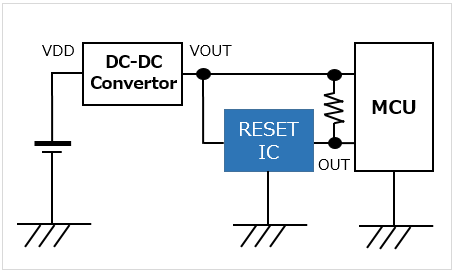 |
Active Low | 12V | IC-PST81 | CMOS output |
ー |
ー |
ー |
PST81□□R□ (SSON-4) |
| PST81□□U□ (SC-82) | ||||||||
| PST81□□N□ (SOT-25) | ||||||||
| IC-PST82 | N-ch open drain |
ー |
ー |
ー |
PST82□□R□ (SSON-4) | |||
| PST82□□U□ (SC-82) | ||||||||
| PST82□□N□ (SOT-25) | ||||||||
| 7V | IC-PST86 | N-ch open drain |
ー |
ー |
ー |
IC-PST86□□R□ (SSON-4) | ||
| IC-PST86□□U□ (SC-82) | ||||||||
| IC-PST86□□N□ (SOT-25) | ||||||||
Separate sensing terminal type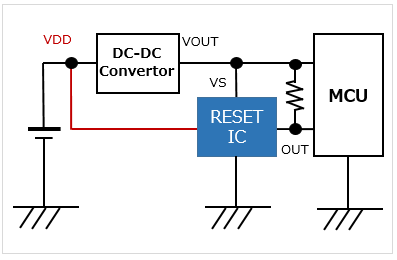 Able to monitor a voltage different from the RESET IC's supply power voltage |
Active Low | 12V | PST851A | CMOS output |
ー |
〇 |
ー |
PST851A□□□R□ (SSON-4) |
| PST851A□□□U□ (SC-82) | ||||||||
| PST851A□□□N□ (SOT-25) | ||||||||
| PST852A | N-chオープンドレイン |
ー |
〇 |
ー |
PST852A□□□R□ (SSON-4) | |||
| PST852A□□□U□ (SC-82) | ||||||||
| PST852A□□□N□ (SOT-25) |
| Configuration example | Output logic | Maximum rating | Series type | Output type |
Delay time |
Separate sensing terminal |
Manual reset |
Series (package) |
With a delay terminal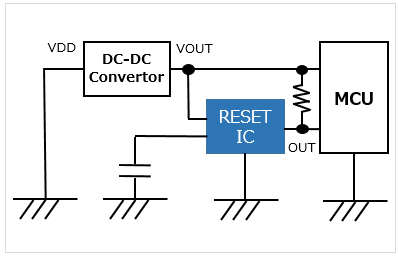 |
Active Low | 12V | IC-PST83 | CMOS output |
External settings |
ー |
ー |
PST83□□R□ (SSON-4) |
| PST83□□U□ (SC-82) | ||||||||
| PST83□□N□ (SOT-25) | ||||||||
| IC-PST84 | N-ch open drain |
External settings |
ー |
ー |
PST84□□R□ (SSON-4) | |||
| PST84□□U□ (SC-82) | ||||||||
| PST84□□N□ (SOT-25) | ||||||||
| 7V | PST893A | CMOS output |
External settings |
ー |
ー |
PST893A□□□R□ (PLP-4) | ||
| PST893A□□□U□ (SC-82) | ||||||||
| PST893A□□□N□ (SOT-25) | ||||||||
| PST894A | N-ch open drain |
External settings |
ー |
ー |
PST894A□□□R□ (PLP-4) | |||
| PST894A□□□U□ (SC-82) | ||||||||
| PST894A□□□N□ (SOT-25) | ||||||||
| PST89DA | CMOS output |
External settings |
ー |
ー |
PST89DA□□□R□ (PLP-4C) | |||
| PST89EA | N-ch open drain |
External settings |
ー |
ー |
PST89EA□□□R□ (PLP-4C) | |||
With a delay terminal/separate sensing terminal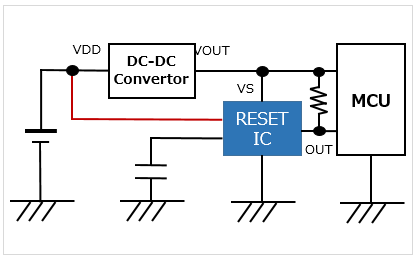 Able to monitor a voltage different from the RESET IC's supply power voltage |
Active Low | 6.5V | PST853A |
CMOS output |
External settings |
〇 |
ー |
PST893R□□□N□ (SOT-25) |
| PST854A |
N-ch open |
External settings |
〇 |
ー |
PST894R□□□N□ (SOT-25) | |||
| Active Low | 40V | PST114 | N-ch open drain |
External settings |
〇 |
ー |
PST114□□□N□ (SOT-26) | |
| Active High | 40V | PST11D | N-ch open drain |
External settings |
〇 |
ー |
PST11D□□□N□ (SOT-26) | |
With a delay pin/manual resetting function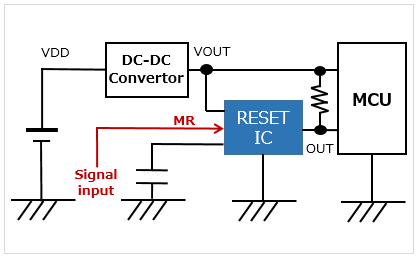 Inputting a signal to the MR pin-outputs a reset signal regardless of the monitored voltage |
Active Low | 6.5V | PST893R |
CMOS output |
External settings |
ー |
〇 |
PST893R□□□N□ (SOT-25) |
| Active Low | 6.5V | PST894R |
N-ch open drain |
External settings |
ー |
〇 |
PST894R□□□N□ (SOT-25) | |
With a delay function (Built-in timer)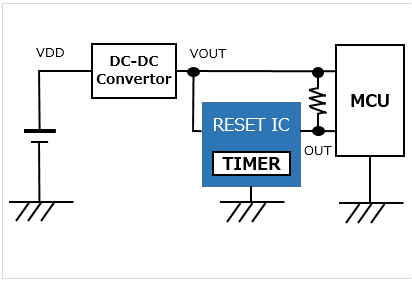 |
Active Low | 7V | PST809 | CMOS output |
Internal settings |
ー |
ー |
PST809□□□□U□ (SC-82) |
| PST809□□□□N□ (SOT-23) | ||||||||
| PST803 | N-ch open drain |
Internal settings |
ー |
ー |
PST803□□□□U□ (SC-82) | |||
| PST803□□□□N□ (SOT-23) | ||||||||
| Active Low | 6V | PST87xA | CMOS output |
Internal settings |
ー |
ー |
PST87□A□□□R□ (SSON-4) | |
| PST87□A□□□U□ (SC-82) | ||||||||
| PST87□A□□□N□ (SOT-23) | ||||||||
| PST88xA | N-ch open drain |
Internal settings |
ー |
ー |
PST88□A□□□R□ (SSON-4) | |||
| PST88□A□□□U□ (SC-82) | ||||||||
| PST88□A□□□N□ (SOT-23) | ||||||||
| Active High | 7V | PST810 | CMOS output |
Internal settings |
ー |
ー |
PST810□□□□U□ (SC-82) | |
| PST810□□□□N□ (SOT-23) | ||||||||
| PST804 | N-ch open drain |
Internal settings |
ー |
ー |
PST804□□□□U□ (SC-82) | |||
| PST804□□□□N□ (SOT-23) | ||||||||
With a delay function (Built-in timer)/manual resetting function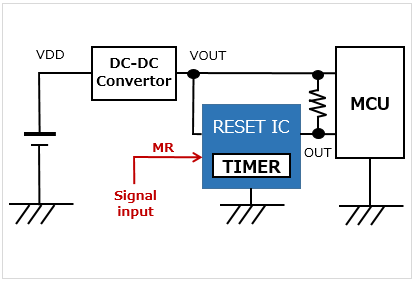 Inputting a signal to the MR terminal outputs a reset signal regardless of the monitored voltage |
Active L | 6V | PST87xR | CMOS output |
Internal settings |
ー |
〇 |
PST87□R□□□R□ (SSON-4) |
| PST87□R□□□U□ (SC-82) | ||||||||
| PST87□R□□□N□ (SOT-25) | ||||||||
| PST88xR | N-ch open drain |
Internal settings |
ー |
〇 |
PST88□R□□□R□ (SSON-4) | |||
| PST88□R□□□U□ (SC-82) | ||||||||
| PST88□R□□□N□ (SOT-25) | ||||||||
| 12V | IC-PST596 | N-ch open drain |
Internal settings/50msec |
ー |
〇 |
PST596□N (SOT-25) | ||
| IC-PST597 | N-ch open drain |
Internal settings/100msec |
ー |
〇 |
PST597□N (SOT-25) | |||
| IC-PST598 | N-ch open drain |
Internal settings/ 200msec |
ー |
〇 |
PST598□N (SOT-25) |
Automotive use Rated voltage: 40 V; RESET IC with a separate sensing pin best for monitoring battery voltage
| Configuration example | Output logic | Maximum rating | Series type | Output type |
Delay time |
Separate sensing pin |
Manual reset |
Series (package) |
With a delay pin / Separate sensing pin / 1ch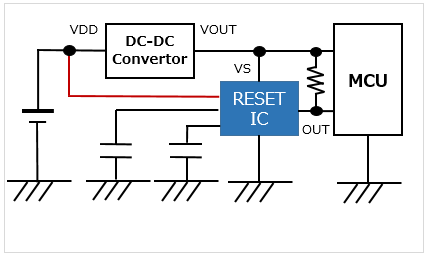 Able to monitor a voltage different from the RESET IC's supply power voltage |
Active Low | 40V | PST114 | N-ch open drain |
External settings |
〇 |
ー |
PST114□□□N□ (SOT-26) |
| Active High | 40V | PST11D | N-ch open drain |
External settings |
〇 |
ー |
PST11D□□□N□ (SOT-26) | |
Without a delay/Separate sensing pin/2ch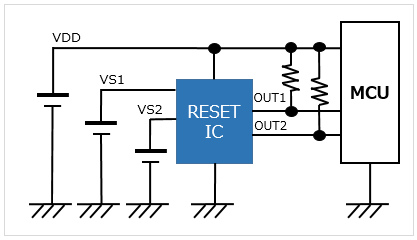 Able to monitor two voltages different from the RESET IC's supply power voltage |
CH1:Active L / CH2:Active L | 40V | PST122A | N-ch open drain |
- |
〇 |
ー |
PST122A□□NRH (SOT-26B) |
| CH1:Active L / CH2:Active H | PST122B | N-ch open drain |
- |
〇 |
ー |
PST122B□□NRH (SOT-26B) | ||
| CH1:Active H / CH2:Active L | 40V | PST122C | N-ch open drain |
- |
〇 |
ー |
PST122C□□NRH (SOT-26B) | |
| CH1:Active H / CH2:Active H | PST122D | N-ch open drain |
- |
〇 |
ー |
PST122D□□NRH (SOT-26B) |
For product-related inquiries, please contact us using the form below.
Related page
Contact Us
Please click the inquiry type below according to your question. Each product / sales representative will respond to you.
