What are the functions of a DC-DC converter?
What are the functions of a DC-DC converter?
Explanations of the main types and what to consider when choosing one

DC-DC converters are devices and components that convert the voltage of a direct-current power supply. MinebeaMitsumi's products include linear regulators and DC-DC switching converters. Various types have been developed for different applications and purposes, and they are essential for devices like smartphones, electric vehicles (EVs), and robot vacuum cleaners that have become indispensable to our daily lives and businesses.
This article introduces the specific types of DC-DC converters available and the situations and applications in which they are used. We will also look at some of the key points to consider when selecting a DC-DC converter.
1. What is a DC-DC converter?
A DC-DC converter is a device that takes one direct current (DC) and converts it to another DC, but its most important function is to convert voltage. In addition to functions such as increasing or decreasing the input voltage to output it, a DC-DC converter also has the ability to output a constant voltage regardless of the input voltage.
This section first explains the purpose of using a DC-DC converter and the differences between it and an AC-DC converter.
Purpose of using a DC-DC converter
Stable voltage is essential for the operation of electronic devices. DC-DC converters are used to regulate and maintain voltage so that electronic devices can operate stably. The use of DC-DC converters is essential because operating electronic devices with the wrong voltage can cause malfunctions and failures.
DC-DC converters are also used to improve the power efficiency of electronic devices that use batteries and to improve the efficiency of battery use.
Differences from AC-DC converters
In addition to DC-DC converters, there are also AC-DC converters. DC-DC converters are devices that convert the voltage of a DC power supply, while AC-DC converters are devices that convert an alternating current (AC) power supply to a DC power supply.
The electrical outlets in most Japanese homes and commercial facilities are set to 100 V AC. On the other hand, many electronic devices are designed to operate on DC, such as 10 V DC or 5 V DC.
Therefore, when you try to run an electronic device from an electrical outlet, you need to convert the alternating current to direct current, and the AC-DC converter is the device that does this.
2. Main types of DC-DC converters
DC-DC converters are broadly divided into two types, namely “linear regulators” and “switching regulators,” depending on the method used to convert the voltage. This section explains the functions, advantages, and disadvantages of each type.
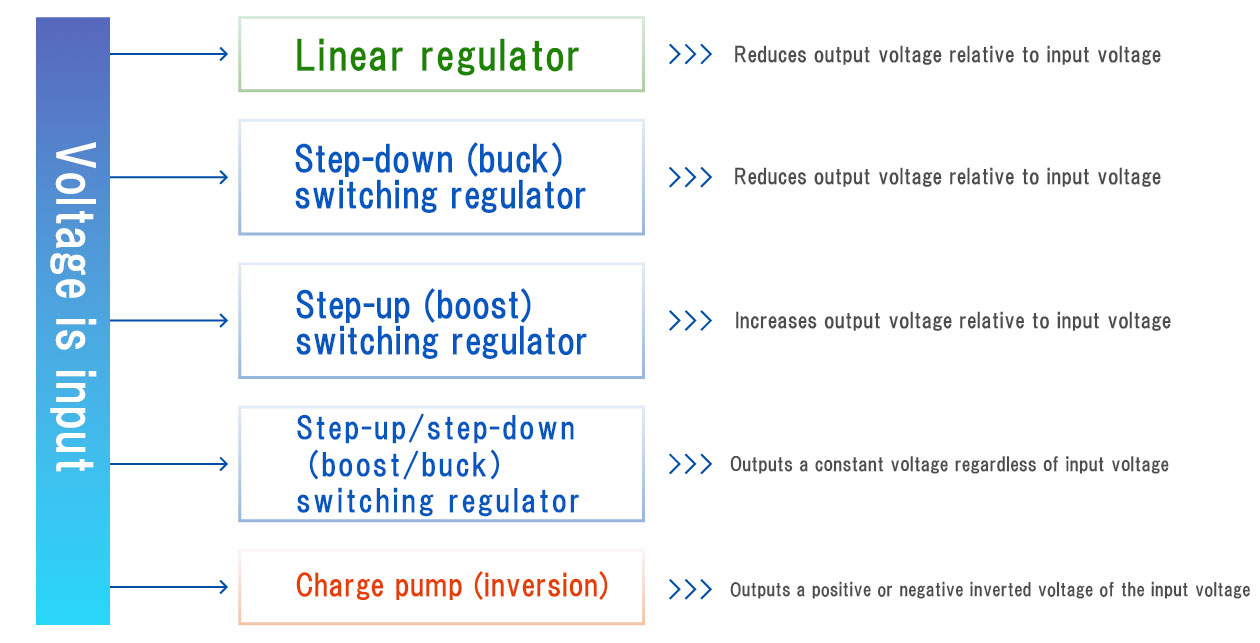
Linear regulator
A linear regulator is a simple DC-DC converter that functions to reduce the output voltage relative to the input voltage. It has a simple structure and appearance, and consists of three terminals for input, output, and ground (GND).
The fact that it has a low power conversion efficiency because excess voltage is dissipated as heat is a disadvantage, but it also has the advantage of being less prone to generating noise.
Switching regulator
A switching regulator is a DC-DC converter that controls voltage by rapidly turning a switch on and off. It was developed to provide more efficient power conversion than linear regulators, and has become the mainstream choice for efficiency, especially in mobile devices.
The advantage of this type of regulator is that it can handle high currents because it dissipates less heat and has a high power conversion efficiency. On the other hand, it has the disadvantage of generating more noise than linear regulators.
Switching regulators can be further subdivided according to their functions. The major types are as follows.
Step-down (buck) regulator
The function of a step-down (buck) regulator is to lower the output voltage relative to the input voltage. For example, it can output a voltage of 3 V DC from an input voltage of 5 V DC.
Step-up (boost) regulator
The function of a step-up (boost) regulator is to increase the output voltage relative to the input voltage. For example, it can output a voltage of 5 V DC from an input voltage of 3 V DC.
Step-up/step-down (boost/buck) regulator
The function of a step-up/down (boost/buck) voltage regulator is to output a constant voltage regardless of the input voltage. For example, it will step up the input voltage from 3 V DC to 5 V DC and output it, and step down the input voltage from 7 V DC to 5 V DC to maintain a constant output voltage.
Charge pump (inversion)
A charge pump is a method of generating an output voltage by transferring an electrical charge and combining the input voltage with the voltage stored in a capacitor. In the inverting type, it can also produce a negative voltage from a positive voltage, for example, to output a voltage of −3 V DC for an input voltage of 3 V DC, and to output a voltage of 3 V DC for an input voltage of −3 V DC.
3. Example of using a DC-DC converter
DC-DC converters, whose main function is voltage control, are used in a wide variety of situations. This section presents some examples of the types of electronic devices in which they are used.
Mobile device
DC-DC converters operate in mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Their main purpose is to optimize the voltage of the batteries installed in these electronic devices.
Household batteries
DC-DC converters are also used in the batteries of household electric appliances such as robot vacuum cleaners, stick vacuum cleaners, electric toothbrushes, and electric shavers. By converting and stabilizing the voltage supplied from the power supply using a DC-DC converter, we can operate household electrical appliances safely. Another characteristic is that reduces anergy wastage.
Automobiles
DC-DC converters are found in automobiles, particularly in electric vehicles (EVs) and hybrid vehicles. They are used to convert the voltage when supplying power from the high-voltage traction battery, which can be considered the EV’s original power supply, to the various low-voltage systems in the vehicle.
Another area that has attracted attention in recent years, in line with the development of automated driving, is the use of DC-DC converters in in-vehicle multimedia, or car infotainment. Car infotainment systems are powered by the in-vehicle battery, but as the wiring comes to an end, the voltage can drop due to factors such as wiring resistance. DC-DC converters compensate for voltage drops due to wiring resistance by converting the input voltage to a stable output voltage.
4. Key points to consider when selecting a DC-DC converter
When selecting a DC-DC converter, you need to consider a number of points. The most important ones are as follows.
Efficiency of voltage output and noise
When selecting a DC-DC converter, we recommend that you check the balance between efficiency and noise when the required voltage is output.
For example, when producing 1.8 V DC from an input voltage of 5 V DC, a linear regulator generates low noise but offers poor efficiency when the voltage differential is large. A switching regulator delivers high efficiency but also high noise, so the choice is between efficiency and noise.
Comparison of linear regulators and switching regulators
Scrollable
|
Noise |
Circuit configuration |
Efficiency |
Heat generation |
Configuration cost |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear regulator | Small | Easy | Poor | High | Low |
| Switching regulator | Large | Complex | Good | Low | High |
-
*A simple comparison between a typical linear regulator and a switching regulator. The assumed conditions are that an output voltage of 1.8 V DC is produced from the input voltage of 3 V DC.
Output current
Check the output current in the DC-DC converter’s data sheet. The key point is whether it can supply the required current at maximum load.
Recommended operating voltage range
The DC-DC converter’s data sheet contains the recommended operating voltage range. You must verify that it covers the entire input voltage range over which the target electronic device expected to be used.
Output voltage range and accuracy
Also check that the output voltage range and output voltage accuracy of the DC-DC converter in question match the voltage required by the device to be powered. If the output voltage range does not match, the device may not run properly.
Switching frequency range
For switching regulators, be sure to check the frequency range. Consult the data sheet to see if it supports the minimum to maximum switching frequencies that can be expected in the operating environment.
5. For help in selecting the right DC-DC converter for your needs or applications, talk to MinebeaMitsumi
There are many different types and applications of DC-DC converters, so choosing the right one can be confusing.
MinebeaMitsumi offers a wide range of DC-DC converters, as well as various power supply ICs that control and monitor power supplies and voltages. If you are having trouble choosing a DC-DC converter and would like to hear the opinions of experts in this field, feel free to contact us.
For product-related inquiries, please contact us using the form below.
Related page
Contact Us
Please click the inquiry type below according to your question. Each product / sales representative will respond to you.