MEMS and the Future of Medical and Nursing Care

One of the global challenges in the medical and nursing care industry in recent years has been the increase in healthcare costs due to demographic changes and rapid urbanization. Furthermore, labor shortages, such as the shortage of doctors, nurses, and caregivers, has also become an issue. Medical DX using information and communications technology (ICT), including IoT, is attracting growing attention and expectations as one way to solve these issues. This section describes some ways of solving these issues in the medical and nursing care industry and the MEMS technology used in this field.
- Challenges Facing the Medical and Nursing Care Industry
- The Medical and Nursing Care Industry and MEMS Sensors
- The Future of the Medical and Nursing Care Industry and MEMS
Challenges Facing the Medical and Nursing Care Industry
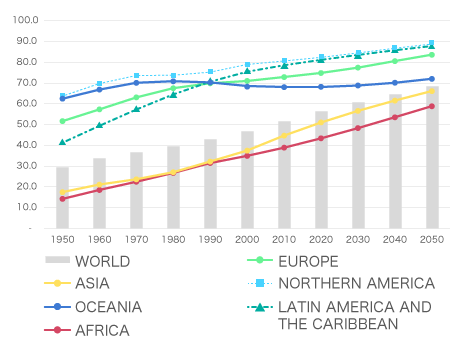
The world population exceeded 8 billion in November 2022 and is expected to reach 8.5 billion by 2030.
As regions with significant population growth, attention has been focused on China and India, but rapid population growth is expected in Africa in the future. Also, as economic development progresses in these regions, urbanization is rapidly advancing and is expected to continue in the future.
Countries undergoing major changes in population growth and urbanization face a variety of challenges, and healthcare is no exception. As countries become more affluent, they are improving their medical care, and as the number of patients increases, so do the issues of rising medical costs and shortages of medical care personnel.
Source: United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2018). World Urbanization Prospects: The 2018 Revision, Online Edition.
License: CC BY 3.0 IGO
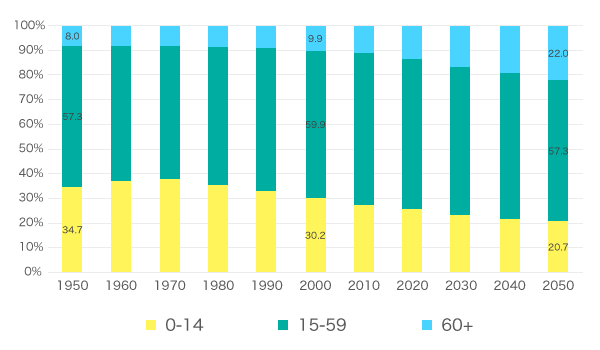
Developed countries are facing an aging society due to the increase in average life expectancy resulting from advances in medical care. Globally, the percentage of the population aged 60 and over, which was less than 10% in 2000, is expected to increase sharply after 2020 and reach 22% by 2050, exceeding the 20.7% of the population aged 14 and under. Demographic changes due to falling birthrates and an aging population are also causing problems such as increased social security costs, including medical expenses, and a shortage of medical and nursing care personnel.
Source: United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2022). World Population Prospects 2022, Online Edition.
License: CC BY 3.0 IGO
Preventive medicine and medical DX are gaining attention as one way to solve these problems. Preventive medicine aims to maintain a state of health that prevents illness from developing, and requires daily observation of changes in one’s physical condition. Also, by accumulating the results as data, it is possible to enable early detection and early treatment of diseases, as well as prevent recurrence and seriousness of illnesses. Various sensing technologies are used in these preventive medicine and medical DX initiatives.
The Medical and Nursing Care Industry and MEMS Sensors
Development of medical DX is needed to solve various problems faced by the medical and nursing care industry. Also, the widespread adoption of medical devices is necessary to realize medical DX, and MEMS is attracting attention as a technology that assists in the spread of such medical devices. This section provides an overview of medical DX and presents application examples of MEMS devices that will support the future of medical care.
Devices Enabling Medical DX
In the medical industry, as mentioned earlier, preventive medicine is also important. To prevent epidemics among patients and support their health more effectively and efficiently, rapid data collection, study, and analysis are required. And, in order to implement medical DX, and various technological reforms are underway.
For example, a stethoscope can now record and play back heartbeats and other sounds that previously could only be heard by a physician, thanks to the advent of digital stethoscopes equipped with MEMS microphones. The ability to record audio information that could not be recorded in the past has made it possible to display the results on a PC monitor or other device, thereby improving the accuracy of diagnosis and facilitating the sharing of information.
Medical Equipment Supporting Decentralized Medicine
Conventional testing equipment is large and extremely expensive, limiting the number of medical institutions that can provide it. However, the use of MEMS has made it possible to downsize and mass-produce these devices, making them accessible to small clinics and hospitals.
For example, a spirometer used to test lung function was a large device that could only be used with the assistance of a nurse. Now, however, with the advent of small spirometers that utilize MEMS technology, it is possible to perform tests at home. The acquired data can be linked to the attending physician over the Internet, leading to early detection of diseases. In this way, tests and medical examinations that were previously available only at certain medical institutions are becoming more accessible through decentralized medicine.
Another example is insulin pump therapy, which was developed as a treatment for diabetes and uses a portable medical pump instead of conventional insulin injections. The pump is controlled by a variety of MEMS sensors, and patients only need to stick a needle connected to the pump once every few days to receive a steady dose of insulin. This not only reduces the burden on the individual, but also lowers the risk of forgotten injections and sudden drops in blood sugar levels. In this way, decentralized medicine is helping to improve the quality of life (QOL) for everyone.
The use of decentralized medicine is also expected to play a key role in rural and remote areas where there are no specialist physicians, and the development of testing equipment with AI-based analysis functions is underway. The widespread use of medical devices is essential to make such treatments and examinations possible, and MEMS is playing a major role in the development of decentralized medicine as a technology for enabling miniaturization and mass production.
Advanced Sensing for Reducing Work Burden
In the nursing care industry, to reduce the work burden on nursing care staff, advanced sensing technology is being used for monitoring patients, and sensor systems that detect abnormalities in a patient’s body are being utilized.
For example, pressure sensors can be attached to beds to analyze a patient’s heart rate and respiration, or ultrasonic sensors can be attached to patients to measure the shape of their bladder. These sensors can be used to reduce the work burden and improve the efficiency of nursing care staff in monitoring and making rounds for checking on patients, thereby helping to alleviate the labor shortage.
In addition to reducing the work burden on nursing care staff, these sensors must also be comfortable for patients. The use of MEMS technology in the development of nursing care equipment will become increasingly important for easing the restrictions on the patient’s actions and body.
The Future of the Medical and Nursing Care Industry and MEMS
Recently, MEMS technology in the medical and nursing care industry has been the subject of various research and development efforts.
In the field of minimally invasive treatment and testing, cellular-level treatment and testing can now be performed at the tips of endoscopes and catheters, and in the non-invasive field, testing using small ultrasonic probes has become a reality. In this way, the introduction of medical devices using MEMS technology is making testing and measurement that before required extensive equipment to be more accessible than ever before.
Also, nursing care robots and medical robots are expected to be a promising field in the future, and in addition to enabling finely detailed work, MEMS technology is being studied for use in detecting small changes that cannot be noticed by humans.
Devices utilizing MEMS are already indispensable in the medical and nursing care field, and further development and growth in demand are expected in the future.
