Designs of shaft and housing
For ball bearing applications, the shaft and housing dimensions and precision should be carefully designed to optimize the performance of the bearing.
Shaft and housing
Finishing accuracy of shaft and housing
When the bearings are installed, roundness of the bearings can be degraded if the accuracy and surface roughness of the shaft and housing are not at satisfactory levels.
Fillet radii of corners of shaft and housing
The side faces of the shafts and housing (areas contacting the bearing's side face) should be perpendicular to the shaft center line and fitting surface.
Also, the maximum permissible radius of the fillet ( r as max) must be smaller than the minimum permissible chamfer dimension of the bearing.
Shoulder height
The shoulder height (h) of the shaft and housing must be larger than the minimum allowable chamfer dimension of the bearing, and it should be a height that firmly contacts the end faces of the outer ring and inner ring.
As a guide, the minimum value of shoulder height (h) is about 4 times the minimum allowable chamfer dimension of the bearing.
Refer to Fig. 11-1 and the table on the right for dimensional relationship.
Excerpt from JIS B 1566
(unit : mm)
Inner ring or outer ring's chamfer dimensions |
Shaft or housing |
||
|---|---|---|---|
Corner radius |
For general use*1 |
For special use*2 |
|
rs min |
ras max |
h (min) |
|
| 0.05*3 | 0.05 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| 0.08*3 | 0.08 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| 0.3 | 0.3 | 1.25 | 1 |
*1 When a large axial load is applied, a shoulder height larger than this value is required.
*2 Used when the axial load is small.
*3 Not specified in JIS B 1566.
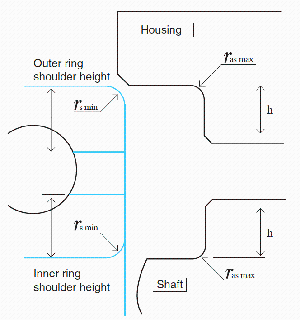
Fig11-1
Related page
Engineering Information for Miniature & small ball bearings
Selecting the Right Part
Technical Data
Contact Us
Please click the inquiry type below according to your question. Each product / sales representative will respond to you.