Product Catalog
The major factor limiting output torque is the temperature of the motor coil. It is therefore necessary to gain an understanding of the temperature characteristics of the motor under conditions of normal usage. Also, the surface area varies according to motor size, and radiation characteristics therefore also naturally vary, leading to changes in motor temperature. The following shows the major characteristics of our motors. Please pay particular attention to this information when selecting a motor.
Coil temperature rise per 1W input
スクロールできます
|
PM15S |
PM20S |
PM20L |
PM25S |
PM25L |
PM35S |
PM35L |
PM42S |
PM42M |
PM42L |
PM55L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 54 | 35 | 31 | 30 | 26 | 19 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 8 |
-
*If input power (W) is multiplied by the relevant value above, you can gain a rough estimate of the coil temperature.
Ratio between motor surface temperature and coil temperature
スクロールできます
|
PM15S |
PM20S |
PM20L |
PM25S |
PM25L |
PM35S |
PM35L |
PM42S |
PM42M |
PM42L |
PM55L |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.9 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.91 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.88 | 0.88 | 0.87 |
-
*If you measure the motor surface temperature and divide that figure by the relevant value above, you can gain a rough estimate of the coil temperature.
Time to reach coil temperature saturation
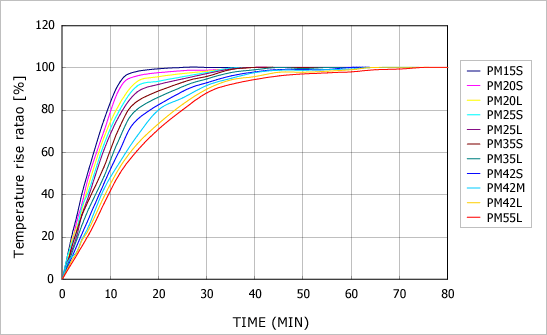
The graph shows the amount of time until the coil reaches saturation temperature. This information allows you to judge when overdrive is possible for a short time, such as when the motor is operating under light duty conditions of use.
Related page
Engineering Information for PM stepping motors
Technical Data
Precautions of Use
Explanation of Technical Terms
Contact Us
Please click the inquiry type below according to your question. Each product / sales representative will respond to you.