Glossary for Technical Terms
- Holding Torque / Max Static Torque
The maximum external torque that can be applied to an energized step motor at 0 pps without causing continuous rotation.
- Detent Torque
The torque required to rotate a non-energized step motor.
This torque results from the magnet of a hybrid or PM rotor motor.
- Step Accuracy
A measure of a step motor's maximum deviation from its desired or indicated position, calculated as a percentage of the step angle. This deviation is non-cumulative, meaning that the deviation found in any number of steps is no greater than the maximum deviation found in a single step.
- Torque / Speed Curve
Curve which shows the correlation between torque and speed.
A curve is for a given motor and a given driver.
- Pulse Rate
Rate that successive pulses are sent or steps are initiated.
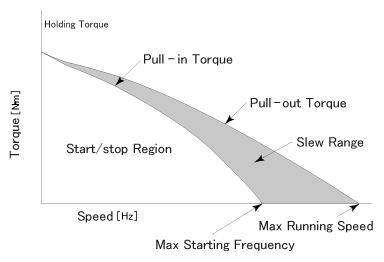
- Start / Stop region
Area on or underneath the pull-in curve. For any load value in this region, the motor can start, stop, or reverse "instantly" (no ramping required) at the corresponding speed value.
- Max Starting Frequency
The frequency where it is possible to synchronize the step motor with its input frequency by accelerating and decelerating.
- Slew Range
The region between the pull-in and pull-out torque curves. A motor may operate in this range, but cannot start, stop or reverse without ramping.
- Max Running Speed
The maximum speed at which the motor can run without losing synchronism or missing steps from a standstill or stop without taking more steps than the pulses.
- Pull-in Torque (Curve)
The maximum torque, for a given speed, where a load can be accelerated into synchronism from a standstill.
- Pull-out Torque (Curve)
The maximum torque that can be applied to a motor operating at a given speed without losing synchronism.
- Resonance
When a motor operated on no load over the entire frequency range, one or more natural oscillating resonance points may be detected.
The range where a motors step rate is near the natural frequency of the motor is called resonance range. A motor operating in this range may experience excessive vibration.
Graph A
Related page
Engineering Information for PM stepping motors
Technical Data
Precautions of Use
Explanation of Technical Terms
Contact Us
Please click the inquiry type below according to your question. Each product / sales representative will respond to you.