What is memory (semiconductor memory)?
What is memory (semiconductor memory)?
Explanations of types, applications, and new technologies
The term “memory” is a general term for electronic components and products that store and memorize various types of data such as programs, and includes magnetic memory, optical disk memory, and semiconductor memory. In addition to memory, there is also storage for holding different types of data, but the main difference between the two is that memory is used for short-term data storage, while storage is used for long-term data storage.
This article explains the types and applications of semiconductor memory, and the key points to consider when choosing what to use in a way that is easy to understand, and also introduces some of the new technologies that are attracting attention.
1. Semiconductor memory is an electronic component or product that uses semiconductor devices to record data
Semiconductor memory is a type of memory that uses semiconductor devices to store data electrically and includes PC memory (DIMM), USB memory, and SD cards.
Semiconductor memory can be broadly divided into two types: volatile memory, in which the recorded data is lost when the power is turned off, and non-volatile memory, in which the data is not lost even when the power is turned off. These two types are used differently, with data such as programs that must not be lost being stored in non-volatile memory, and only the data needed to run the program being read into volatile memory.
■ Classification of semiconductor memory
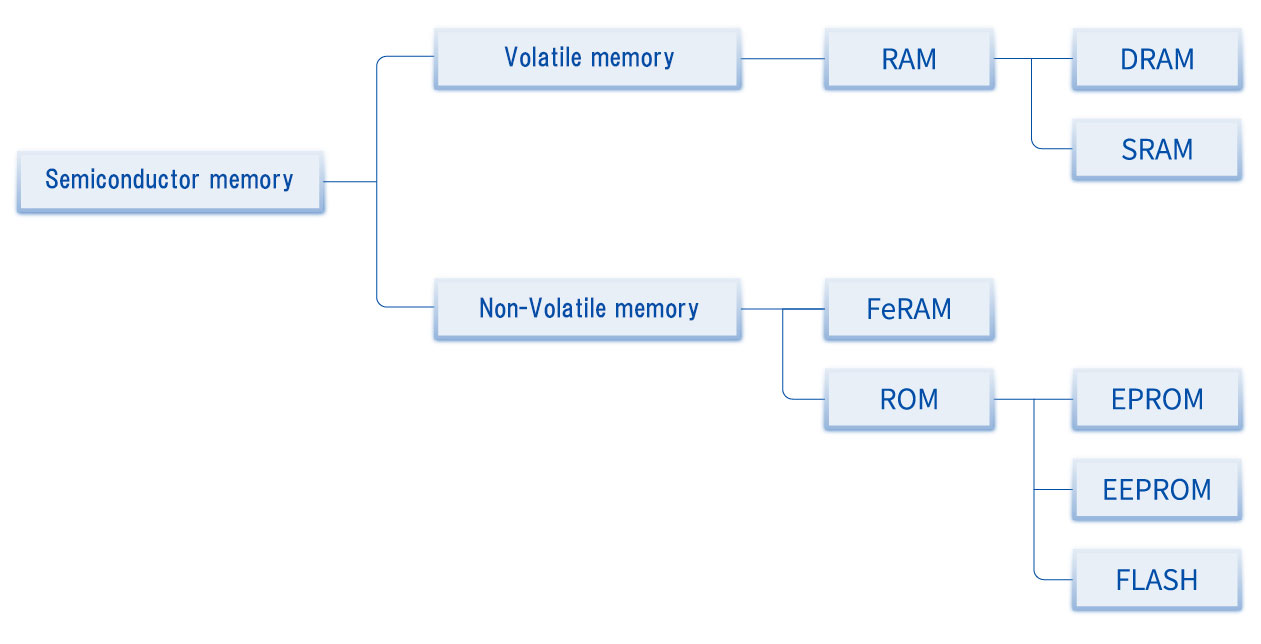
Types of volatile memory
Volatile memory is Random Access Memory (RAM) that can read and write data, and RAM is further divided into DRAM and SRAM. The “D” in DRAM stands for “Dynamic,” and the “S” in SRAM stands for “Static.”
DRAM stores data as electrical charges, but has the characteristic that the charges leak out over time, making it impossible to read the data accurately. For this reason, to maintain the information, a refresh operation is performed periodically to write the same content.
In contrast, SRAM has a logic circuit called a flip-flop that can hold information, so it does not need to be refreshed. For this reason, SRAM is more expensive than DRAM, but is characterized by high operating speed and low power consumption.
Types of non-volatile memory
The most typical type of non-volatile memory is Read Only Memory (ROM), which, as the name implies, is read only. Now, however, rewritable ROM has been developed and is called things like “Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory (EPROM).”
EEPROM is a memory type that has evolved further from EPROM to allow data to be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The first E is the first letter of “Electrically,” and EEPROM is sometimes written as “E2PROM.”
The structure of “FLASH (hereafter, “flash memory”)” is similar to that of EEPROM, and they also share the common feature that data can be erased and reprogrammed electrically; however, flash memory can read and erase data faster than EEPROM. Flash memory is widely used because it is cheaper than EEPROM and can be mass produced.
Most non-volatile memory is of the ROM type, but RAM type also exists. Ferroelectric Random Access Memory (FeRAM) is a non-volatile RAM-type memory that has the following characteristics: high write speed, large number of rewrites, and low power consumption compared to ROM-type memory such as EEPROM.
2. Applications of volatile and non-volatile memory
Volatile and non-volatile memory are used differently depending on their characteristics, and they are sometimes used in combination. This section introduces the applications of volatile memory and non-volatile memory, as well as combined applications of them.
Applications of volatile memory
Applications of DRAM and SRAM volatile memory include the transfer and storage of data within a PC. In this case, DRAM is primarily used as main memory, and SRAM is used as cache memory for the CPU, which is the brain of the PC.
This is because the processing speed of the CPU is very fast, and there is a difference in processing speed when it interacts directly with DRAM. For this reason, SRAM is placed between the CPU and DRAM as cache memory to enable high-speed processing by the CPU.
Applications of non-volatile memory
ROM, a typical example of non-volatile memory, is used to store basic data that is built into devices during manufacture because of its read-only characteristics. For example, it is used to store BIOS and firmware for PCs, as well as the fixed programs that run household appliances such as washing machines and rice cookers, and the implementation of so-called embedded systems.
In contrast, EEPROM and flash memory are employed in a wide range of situations because the data can be rewritten.
For example, EEPROM is used for storing and accessing small data sets. Specifically, it is used in automobiles, portable medical devices, wearable devices, network switches, etc. On the other hand, flash memory is also utilized in high-capacity data storage, such as SSDs, because increasing its capacity is easy.
Combined applications of volatile and non-volatile memory
Since each type of memory has its own characteristics, using a combination of them can improve a product’s overall performance and capabilities.
For example, volatile memory such as SRAM and DRAM can be used for the CPU cache memory and main memory, while non-volatile memory such as flash memory can be used for storage.
3. Key points to consider when choosing memory
There is a number of things to consider when choosing a memory. In this section, we will take a closer look at three of them.
Memory capacity
Memory capacity refers to the amount of data that can be stored and saved. For example, the main memory of a PC or USB memory device is displayed as 8 GB or 16 GB, while SSD memory is displayed as 500 GB or 1 TB.
The processing speed of a PC increases with the number of cores and the clock speed. In addition, the overall processing speed increases with the capacity of the main memory, so memory capacity is a factor directly linked to a PC's performance.
Access speed
Access speed is a metric of the speed at which data is read and written. In the case of SRAM and DRAM, it is expressed as 2,666 MHz, etc.
On the other hand, the speed of flash memory devices such as SD cards is expressed in a form such as 60 MB/s, and classified in increments of speed. A PC that can read and write data quickly can operate smoothly.
Durability
The key to checking the durability of memory is to see if the Total Bytes Written (TBW) value, which indicates the total capacity of writable data, is high.
Non-volatile memory, such as flash memory, is very durable and has the characteristic of being suitable for use as storage, such as in SSDs.
4. Hot new technologies related to memory
In recent years, technological innovations aimed at increasing memory capacity have progressed in line with the rise in the amount of data being handled. This section introduces some of the new technologies attracting attention.
3D NAND flash memory
3D NAND flash memory is a variety of non-volatile memory that uses technology to increase capacity by stacking layers in three dimensions.
Products with more than 200 layers are currently available, and products with more than 400 layers are under development. In addition to high-density data storage, it is mainly used in SSDs and USB memory.
PCM
Phase Change Memory (PCM) is a type of non-volatile memory that uses the difference in electrical resistance between the crystalline and non-crystalline (amorphous) phases of a substance to record data.
It is considered to be faster than flash memory, and is used in storage that requires high-speed data access, as well as in cache memory
MRAM
Magnetoresistive Random Access Memory (MRAM) is a type of non-volatile memory that utilizes the fact that the electrical resistance of the memory cell changes depending on the direction of the magnetism.
It is used in embedded systems for electronic devices and other situations that require low power consumption and high-speed access.
ReRAM
Resistive Random Access Memory (ReRAM) is a form of non-volatile memory that records data based on the resulting resistance difference when a voltage is applied to a metal oxide film sandwiched between electrodes.
It is used in storage that requires durability and high-speed writing, and in IoT devices.
Chiplet
In addition to memory, makers of various types of semiconductors (ICs and chips) have sought high integration through miniaturization and layering of devices and circuits, but in recent years other approaches have emerged. One of these is “chiplets.”
Instead of packing many functions into a single chip through miniaturization and layering, the chiplet achieves large-scale integration and high performance by deliberately dividing the chip into multiple parts and connecting them. The suffix “let” means “small” in English.
5. For all your memory needs, talk to MinebeaMitsumi
Memory (semiconductor memory) is essential to a wide range of electronic devices and is an area where technological innovation is expected to march forward relentlessly. ABLIC, a MinebeaMitsumi Group company, offers a particularly comprehensive lineup of EEPROMs, offering high-quality products that support a wide range of applications. In particular, ABLIC has one of Japan’s largest domestic market shares for in-vehicle serial EEPROMs.
If you have any concerns about semiconductors or are considering specific applications, talk to MinebeaMitsumi today.
For product-related inquiries, please contact us using the form below.
Related page
Engineering Information for Semiconductors
Basic Knowledge
Technical Data
Contact Us
Please click the inquiry type below according to your question. Each product / sales representative will respond to you.