Trouble Symptoms, Causes and Countermeasures
In the event of an abnormality in the equipment incorporating the ball bearing, or damage or breakage of the ball bearing, the cause can be investigated based on the symptoms and conditions. The following shows typical abnormalities and countermeasures.
Abnormal symptoms and conditions
| Symptoms and conditions | Bearing damage, assumed cause, etc. | Damage example | Countermeasures | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abnormal sound |
Continuous sound |
Raceway brinelling | 3 | Reviewing handling of bearings, assembling and transporting equipment(whether excessive load or impact load is applied) |
| Roughness and wear | 1 | Reviewing lubricant, bearing size, preload and seal | ||
| Scratches due to foreign matter in the raceway (indentation) | 2 | Using seal for bearings and reviewing work environment | ||
| Fretting | 4 | Reviewing vibration elimination, packaging and transportation | ||
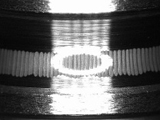
| Electrical arc pitting | 6 | Insulation: Make the ball ceramic | ||
| Component resonance | Reviewing dimensions (thickness) and material of components | |||
| Variable sound |
When the ball is scratched | Reviewing work environment and work(whether foreign matter is intruding or excessive load is applied) | ||
| Biting of foreign matter | Using seal for bearings and reviewing work environment | |||
| Insufficient preload | Reviewing preload amount based on load, rotation conditions, etc. | |||
| Rotation failure |
Does not rotate or rotation is heavy |
Effect (amount, type) of lubricant (grease) | Reviewing grease Improvement of driving parts (motor parts, etc.) (increase the driving power, etc.) |
|
| Foreign matter penetration, adhesive penetration | Reviewing usage environment and work methods | |||
| Large interference | Reviewing fits | |||
| Out of lubrication | Reviewing lubricants and increasing the amount of grease Reviewing the grease type and amount |
|||
| Flaking | 8 | Checking load and rotation conditions Selecting a larger bearing |
||
| Component contact | Reviewing work and design | |||
| Heat generation |
Incorrect grease type and filling amount | Reviewing grease | ||
| Overload | Reviewing load capacity and fits | |||
| Short life | Unsuitable environment, usage conditions, etc. | Reviewing environment and usage conditions | ||
| Large vibration and runout |
Misalignment | Reviewing component dimensional tolerance, cleanliness and process | ||
| Deformation of track surface | Reviewing machining precision (roundness) of shaft or housing Reviewing adhesives and bonding work |
|||
| Improper preload Preload reduction | Reviewing preload amount based on load, rotation conditions, etc. | |||
| Excessive internal clearance | Reducing bearing internal clearance | |||
| Creep | 5 | Reviewing fits | ||
| Grease leakage | Incorrect grease type and filling amount | Reviewing grease | ||
| Incorrect selection of shield/seal | Reviewing shield and seal | |||
| Damaged (cracked) resin material | Chemical attack | 7 | Reviewing lubricants, relieving stress and reselecting resin | |
| Excessive interference | Reviewing fits | |||
| Weld line | Reviewing molding conditions and gate position | |||
Note: Damages are numbered in order of frequency of occurrence
Damage example
| 1 Roughness | 2 Scratches due to foreign matter | 3 Indentation (brinelling) |
|---|---|---|
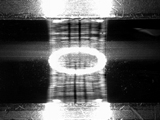 |
 |
 ○: Brineling |
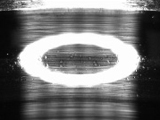
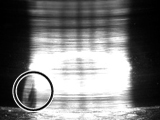
| 4 Fretting | 5 Creep | 6 Electric corrosion(Arcing) |
|---|---|---|
 ○: Fretting |
 |
 |
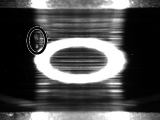
| 7 Chemical attack | 8 Flaking (peeling due to metal fatigue) |
|---|---|
 ○: Chemical attack |

|
Related page
Engineering Information for Miniature & small ball bearings
Selecting the Right Part
Technical Data
Contact Us
Please click the inquiry type below according to your question. Each product / sales representative will respond to you.